
Cold Rolled Steel, commonly known as CRS steel, is a fundamental material in modern manufacturing and construction. Known for its enhanced surface finish, precise dimensions, and improved mechanical properties, cold rolled steel is widely used across various industries. This article explores what CRS steel is, how it differs from other steel types, its key properties, and the major applications where CRS steel is preferred.
CRS steel refers to steel that has undergone a cold rolling process after it has been hot rolled and cooled. The cold rolling involves passing the steel through rollers at room temperature, which compresses and smooths the steel, improving its surface quality and dimensional accuracy.
Compared to hot rolled steel, cold rolled steel features:
This makes CRS steel ideal for applications requiring precision and high-quality surface appearance.
Cold rolling involves several key steps:
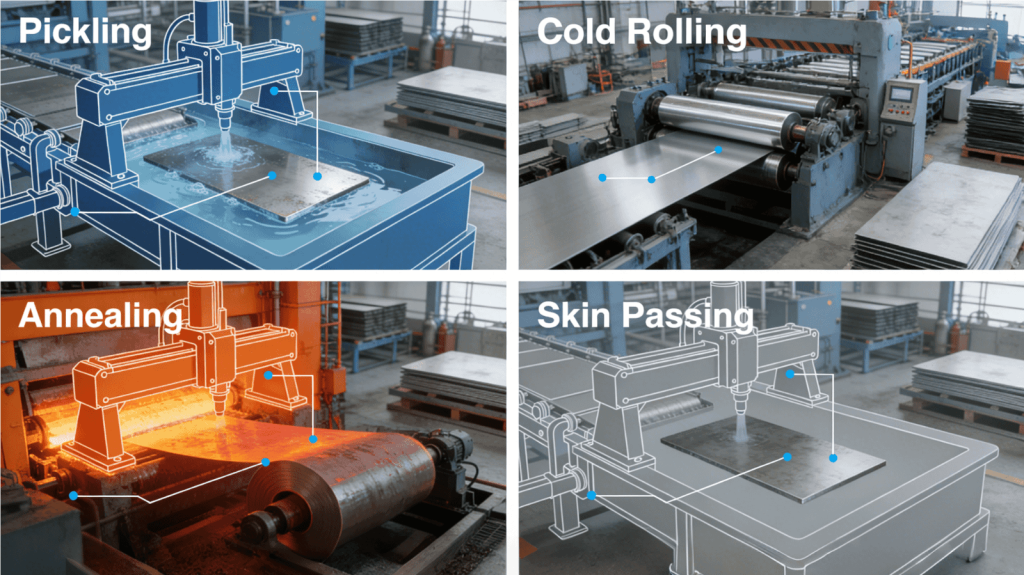
This process enhances mechanical strength and surface quality, making CRS steel suitable for tight tolerance applications.
The cold rolling process imparts several important properties to CRS steel:
The ability to control thickness down to very fine tolerances makes CRS steel the material of choice where precision is critical.
CRS steel is used extensively in industries that demand precision, strength, and quality finishes:
CRS steel is widely used for manufacturing body panels, chassis components, and interior parts due to its excellent surface finish and strength, which supports deep drawing and stamping operations.
From refrigerator cabinets to washing machine panels, CRS steel provides a smooth, paintable surface and consistent thickness necessary for high-volume production.
CRS steel is used in metal framing, roofing panels, and decorative trim, where strength and appearance matter.
Its surface finish and mechanical properties make CRS steel suitable for control panels, server racks, and electrical housings.
Office furniture, lockers, and shelving units often use cold rolled steel for its durability and aesthetic quality.
Choosing CRS steel offers multiple benefits:
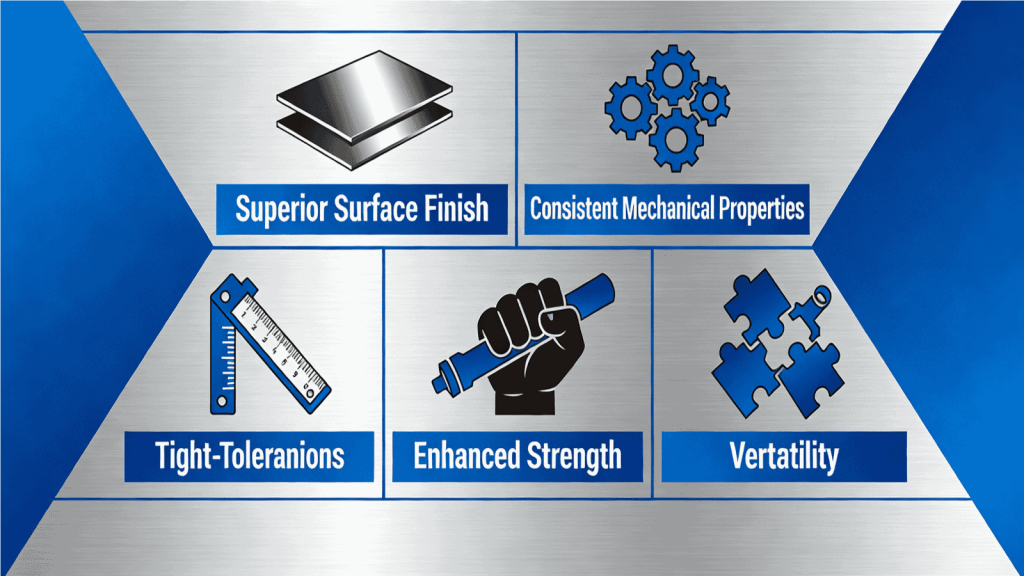
These advantages explain why cold rolled steel is often preferred over hot rolled steel for high-quality and precision applications.
While both start from the same raw steel, their finishing processes and resulting properties differ:
| Feature | CRS Steel (Cold Rolled) | Hot Rolled Steel |
| Surface Finish | Smooth, clean | Rough, scaled |
| Dimensional Tolerance | Tight, precise | Looser |
| Mechanical Properties | Higher strength, strain hardened | Lower strength |
| Typical Applications | Automotive, appliances, furniture | Structural, heavy fabrication |
Cold rolled steel’s refined qualities make it ideal where appearance and precision matter, while hot rolled steel suits heavy-duty, less visible uses.
CRS steel (cold rolled steel) is a versatile, high-quality material widely used across automotive, appliance, construction, and manufacturing industries. Its smooth surface, precise dimensions, and enhanced mechanical properties provide advantages over hot rolled steel in applications requiring strength, formability, and aesthetic appeal.
Understanding the cold rolling process and the properties of CRS steel helps engineers and buyers specify the right material for their projects, ensuring durability, performance, and cost efficiency.

Walmay will help match the right stainless product form and specification for your application, confirm quantities and packing needs, and provide requested documents based on order requirements.